Dental terminology is explained‚ removing intimidation‚ crucial for all medical fields; a foundational understanding is presented‚ as detailed in resources like DOKUMEN.PUB.
Defining Dental Terminology
Dental terminology represents a specialized language within the broader medical field‚ demanding precise communication among professionals. Resources‚ such as those found on DOKUMEN.PUB‚ highlight its importance. It’s built upon root words‚ prefixes‚ and suffixes‚ creating a systematic way to describe anatomical structures‚ procedures‚ and conditions.
Understanding these components is key to deciphering complex medical records and ensuring accurate patient care. This specialized vocabulary facilitates clear documentation‚ effective treatment planning‚ and seamless collaboration within dental teams. Mastering this language is fundamental for success.
Importance of Accurate Terminology
Accurate dental terminology is paramount for effective patient care and legal documentation. Misinterpretation can lead to incorrect diagnoses‚ inappropriate treatments‚ and potential malpractice claims. Resources like those detailed on DOKUMEN.PUB emphasize this critical need for precision.
Clear communication between dentists‚ hygienists‚ and other healthcare providers relies on a shared understanding of these terms. Consistent and standardized language minimizes errors‚ enhances collaboration‚ and ultimately safeguards patient well-being. Proper terminology ensures a cohesive and safe dental environment.
Root Words‚ Prefixes‚ and Suffixes
Dental terminology is built upon root words‚ prefixes‚ and suffixes‚ enabling comprehension of complex terms. Understanding these components‚ as highlighted in resources like DOKUMEN.PUB‚ unlocks the meaning behind medical jargon. For example‚ “gingivo-” relates to gums‚ while “-itis” signifies inflammation.
Breaking down words into these parts simplifies learning and improves recall. Mastering these elements allows for accurate interpretation and effective communication within the dental profession‚ fostering clarity and precision.

Anatomy and Oral Structures
Dental terminology requires knowledge of oral cavity components; understanding anatomical structures is fundamental‚ as detailed in resources like DOKUMEN.PUB‚ for accurate descriptions.
Oral Cavity Components
Understanding the oral cavity’s components is vital when learning dental terminology. This complex area includes the lips‚ cheeks‚ palate – both hard and soft – and the tongue‚ all contributing to speech and mastication. The teeth themselves‚ embedded in alveolar processes‚ are key. Salivary glands produce saliva‚ aiding digestion and protecting tissues;
Furthermore‚ the floor of the mouth and the oropharynx complete this intricate system. Accurate terminology describing these structures‚ as found in resources like DOKUMEN.PUB‚ is essential for clear communication among dental professionals‚ ensuring precise diagnoses and treatment planning. Mastering these terms builds a strong foundation.
Dental Quadrants and Tooth Numbering Systems
Dental charting relies on standardized numbering systems for accurate record-keeping. The mouth is divided into four quadrants: upper right‚ upper left‚ lower right‚ and lower left. Several systems exist‚ including the Universal Numbering System (1-32)‚ where each tooth receives a unique number.
The FDI World Dental Federation system uses a two-digit number per quadrant. Understanding these systems‚ detailed in resources like DOKUMEN.PUB‚ is crucial for interpreting dental records and communicating effectively. Precise identification of each tooth is paramount for diagnosis and treatment planning within the oral cavity.
Temporomandibular Joint (TMJ)
The temporomandibular joint (TMJ) connects the mandible (jawbone) to the skull‚ enabling jaw movement essential for speech and eating. Terminology surrounding the TMJ often includes descriptions of dysfunction‚ such as clicking‚ popping‚ or limited range of motion.
Understanding related terms – condyle‚ articular disc‚ and masseter muscle – is vital. Resources like DOKUMEN.PUB provide detailed explanations. Accurate terminology aids in diagnosing and treating TMJ disorders‚ impacting a patient’s overall oral and facial health and comfort.
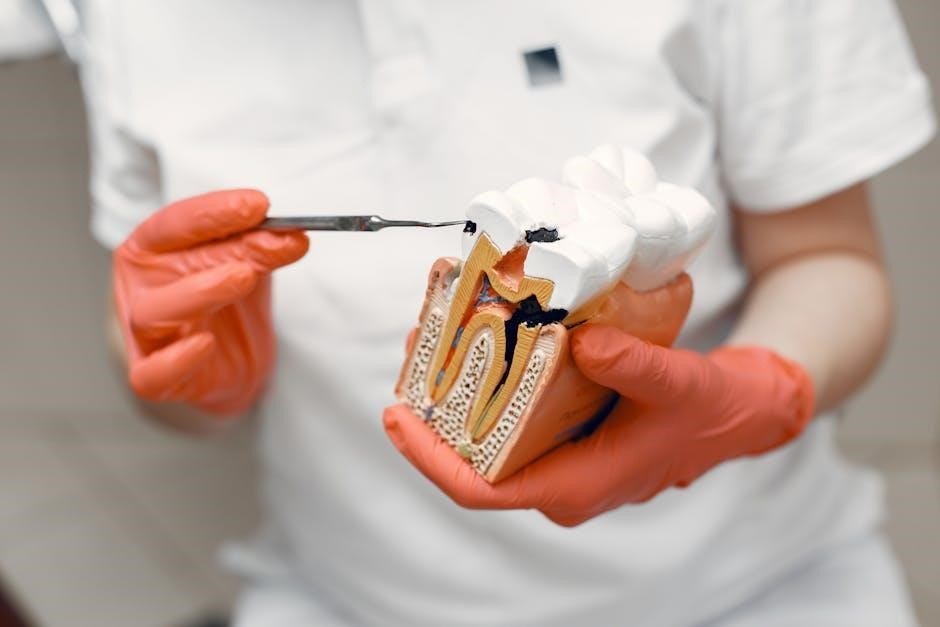
Tooth Origin and Formation
Tooth development stages‚ from initiation to eruption‚ are key concepts; DOKUMEN.PUB details these processes‚ alongside terminology for enamel‚ dentin‚ and pulp formation.
Tooth Development Stages
Understanding tooth development requires grasping distinct stages: initiation‚ budding‚ cap‚ bell‚ and apposition. These phases‚ detailed within dental terminology resources like DOKUMEN.PUB‚ outline the complex journey from cellular signals to fully formed teeth. Initiation marks the beginning‚ budding shows the first sign of tooth shape‚ and the cap stage defines a deeper enamel organ.
The bell stage is crucial for histodifferentiation‚ while apposition involves the deposition of hard tissues – enamel and dentin. These stages are vital for comprehending anomalies and proper dental care‚ all explained through precise terminology.
Enamel‚ Dentin‚ and Pulp
Enamel‚ the outermost layer‚ is a highly mineralized‚ protective covering. Dentin‚ beneath enamel‚ forms the bulk of the tooth‚ offering support. Pulp‚ the innermost core‚ contains nerves and blood vessels‚ vital for tooth vitality. Resources like DOKUMEN.PUB detail these structures using specific dental terminology.
Understanding their composition – hydroxyapatite in enamel‚ collagen in dentin – is crucial. Proper terminology aids in diagnosing issues affecting each layer‚ ensuring effective treatment and patient care‚ as outlined in comprehensive dental guides.
Cementum and Periodontal Ligament
Cementum‚ a bone-like substance‚ covers the tooth root‚ aiding attachment to the periodontal ligament. The periodontal ligament (PDL) connects cementum to the alveolar bone‚ providing crucial support and shock absorption. DOKUMEN.PUB resources emphasize precise terminology when discussing these structures.
Understanding their roles is vital for diagnosing periodontal diseases. Accurate terminology facilitates communication regarding cementum abnormalities or PDL inflammation‚ ensuring appropriate treatment planning and improved patient outcomes‚ as detailed in dental texts.
Practice and Facility Setups
Dental office layouts‚ sterilization areas‚ and equipment are key components‚ requiring precise terminology for effective communication‚ as outlined in dental resources.
Dental Office Layout
A well-planned dental office prioritizes patient flow and efficient operatory use. Reception and waiting areas establish initial impressions‚ while sterilization zones maintain hygiene standards. Operatories—treatment rooms—require specific equipment placement for optimal access. Layout considerations include infection control protocols‚ accessibility for patients with disabilities‚ and adherence to regulatory guidelines. Effective space utilization maximizes functionality‚ ensuring smooth workflows for dental professionals. Understanding dental terminology is vital when discussing these layouts‚ referencing specific areas and equipment accurately. Resources like DOKUMEN.PUB emphasize this need for precise communication within the dental environment.
Sterilization and Disinfection Areas
Dedicated areas for sterilization and disinfection are paramount in dental practices‚ ensuring patient safety and preventing cross-contamination. These zones require specific layouts adhering to strict protocols. Sterilization eliminates all microorganisms‚ utilizing autoclaves and other validated methods. Disinfection reduces microbial load on surfaces. Proper handling of instruments‚ utilizing correct dental terminology for procedures and equipment‚ is crucial. Resources like DOKUMEN.PUB highlight the importance of understanding these processes. Maintaining detailed records of sterilization cycles is essential for compliance and quality assurance within the dental facility.
Equipment and Instrumentation
Dental practices rely on a diverse range of specialized equipment and instrumentation. Understanding the correct dental terminology for each tool is vital for effective communication and treatment. This includes handpieces‚ drills‚ scalers‚ and various instruments used for restorative and surgical procedures. Proper maintenance and sterilization‚ as detailed in resources like DOKUMEN.PUB‚ are essential. Modern dental offices also incorporate digital technologies like intraoral cameras and CAD/CAM systems. Accurate identification and usage of this equipment‚ coupled with precise terminology‚ ensures optimal patient care and efficient workflow.
Infection Control
Infection control protocols‚ including standard precautions and PPE‚ are paramount in dental settings‚ ensuring patient and staff safety‚ as outlined in resources.
Standard Precautions
Standard precautions represent a foundational element of infection control within dental practices‚ treating all patients as potentially infectious. This approach minimizes the risk of transmission of pathogens‚ encompassing bloodborne and body fluid-borne diseases. Key components include hand hygiene‚ utilizing personal protective equipment – gloves‚ masks‚ eyewear‚ and gowns – and safe injection practices.
Proper handling and disposal of sharps‚ respiratory hygiene‚ and meticulous cleaning and disinfection of surfaces are also critical. Adhering to these guidelines protects both dental healthcare personnel and patients‚ creating a safer treatment environment‚ as detailed in dental terminology resources.
Personal Protective Equipment (PPE)
Personal Protective Equipment (PPE) is vital in dental settings‚ forming a barrier against potential exposure to infectious materials. Essential PPE includes gloves‚ protecting hands from contamination; masks and respirators‚ safeguarding the respiratory system; and protective eyewear‚ shielding eyes from splashes and aerosols. Gowns provide a body barrier‚ preventing clothing contamination.
Correct donning and doffing procedures are crucial to avoid self-contamination. Proper selection‚ use‚ and disposal of PPE‚ as outlined in dental terminology guides‚ are fundamental to infection control protocols‚ ensuring a safe environment for both patients and dental professionals.
Sterilization Methods
Sterilization is paramount in dentistry‚ eliminating all microorganisms‚ including spores. Common methods include steam autoclaving‚ utilizing high-pressure saturated steam; dry heat sterilization‚ employing high temperatures for a prolonged duration; and chemical sterilization‚ using liquid or gaseous agents.
Each method requires specific protocols for loading‚ operating‚ and monitoring to ensure effectiveness. Understanding sterilization terminology‚ as found in dental resources‚ is crucial for proper instrument processing‚ preventing cross-contamination and maintaining patient safety within the dental facility.

Emergency Care
Emergency dental care involves trauma management‚ addressing avulsions‚ luxations‚ and soft tissue injuries – critical knowledge for immediate intervention and patient well-being.
Trauma Management
Trauma management in dentistry necessitates a swift and systematic approach to injuries affecting the oral and maxillofacial regions. This includes assessing the extent of damage to teeth‚ supporting structures‚ and surrounding soft tissues. Immediate actions prioritize controlling hemorrhage‚ stabilizing fractures‚ and preventing further injury.
Understanding dental terminology is paramount for accurate documentation and communication amongst the dental team and other healthcare professionals. Proper charting of injuries‚ including tooth fractures‚ dislocations‚ and alveolar bone damage‚ is essential for treatment planning and legal purposes. Effective trauma management aims to preserve tooth structure‚ restore function‚ and minimize long-term complications.
Avulsion and Luxation
Avulsion‚ the complete displacement of a tooth from its socket‚ and luxation‚ the displacement without complete separation‚ represent critical dental emergencies. Immediate intervention significantly impacts prognosis. Accurate terminology – describing the degree of luxation (e.g.‚ Grade I‚ II‚ III) – is vital for treatment decisions.
Successful replantation of avulsed teeth hinges on prompt action and proper handling. Understanding terms like ‘dry time’ and appropriate storage mediums (e.g.‚ Hank’s Balanced Salt Solution) is crucial. Detailed documentation‚ utilizing precise dental terminology‚ ensures continuity of care and optimal patient outcomes following these traumatic injuries.
Soft Tissue Injuries
Soft tissue injuries within the oral cavity‚ encompassing lacerations‚ contusions‚ and abrasions to the lips‚ tongue‚ gingiva‚ and buccal mucosa‚ require careful assessment and management. Precise terminology – differentiating between superficial and deep lacerations‚ for example – guides treatment planning.
Documentation should detail the extent and location of the injury‚ utilizing standardized descriptive terms. Understanding terms like ‘hematoma’ and ‘ulceration’ is essential. Prompt attention to soft tissue trauma minimizes complications like infection and scarring‚ ensuring optimal healing and patient comfort following these often-painful incidents.

Examination and Prevention
Dental charting and radiographic techniques are key components‚ alongside prophylaxis and fluoride treatment‚ for preventative care‚ as outlined in dental terminology resources.
Dental Charting
Dental charting is a fundamental aspect of patient record-keeping‚ utilizing a standardized system to document the condition of each tooth. This precise record includes notations for existing restorations‚ cavities‚ missing teeth‚ and any anomalies observed during a clinical examination.
Accurate charting relies heavily on a strong grasp of dental terminology‚ ensuring clear communication among dental professionals. Charts visually represent the oral health status‚ aiding in treatment planning and tracking progress over time. Resources like those found in dental terminology PDFs emphasize the importance of consistent and detailed charting practices for optimal patient care and legal documentation.
Radiographic Techniques
Radiographic techniques are essential diagnostic tools in dentistry‚ utilizing X-rays to visualize structures not visible during a clinical exam. Understanding the dental terminology associated with radiographic findings – such as periapical lucency or alveolar bone loss – is crucial for accurate interpretation.
Various techniques‚ including bitewing‚ periapical‚ and panoramic radiographs‚ provide different perspectives of the oral cavity. Dental terminology PDFs often include detailed explanations of these techniques and the associated anatomical landmarks. Proper technique and interpretation‚ guided by precise terminology‚ are vital for effective diagnosis and treatment planning.
Prophylaxis and Fluoride Treatment
Prophylaxis‚ or preventative dental care‚ involves removing plaque and calculus to maintain oral health. Dental terminology PDFs detail procedures like scaling and root planing‚ crucial for preventing periodontal disease. Understanding terms like ‘gingivitis’ and ‘periodontitis’ is essential for charting and treatment planning.
Fluoride treatment strengthens enamel and prevents caries. Terms like ‘fluorosis’ and ‘topical fluoride’ are commonly found in dental terminology resources. Accurate documentation‚ utilizing precise terminology‚ ensures consistent and effective preventative care‚ as outlined in comprehensive dental guides.
Pain Management and Pharmacology
Dental terminology PDFs cover local anesthetics‚ analgesics‚ and antibiotics; understanding drug classifications and their effects is vital for effective patient care.
Local Anesthetics
Dental terminology resources‚ often found in PDF format‚ detail local anesthetics as crucial for pain-free dental procedures. These agents temporarily block nerve transmission‚ preventing pain signals from reaching the brain. Understanding classifications – amides and esters – is key‚ alongside knowledge of vasoconstrictors like epinephrine‚ which prolong anesthetic effects and reduce bleeding.
PDFs explain dosage considerations‚ potential adverse reactions‚ and contraindications for each anesthetic type. Proper terminology ensures clear communication regarding patient allergies‚ medical histories‚ and appropriate drug selection. Mastering these terms is fundamental for safe and effective pain management in dentistry.
Analgesics
Dental terminology PDFs clarify the distinction between analgesics and anesthetics; analgesics relieve pain‚ but don’t eliminate sensation. Resources categorize analgesics – non-opioids like NSAIDs (ibuprofen‚ naproxen) and opioids for severe pain. Understanding pharmacological actions‚ indications‚ and contraindications is vital‚ as detailed in comprehensive dental terminology guides.
PDFs emphasize proper dosage calculations and patient education regarding potential side effects. Accurate terminology facilitates clear communication about pain levels‚ treatment plans‚ and medication management. Knowledge of analgesic classifications ensures appropriate pain control strategies are implemented effectively.
Antibiotics
Dental terminology PDFs detail antibiotic classifications – penicillin‚ tetracycline‚ macrolides – crucial for treating bacterial infections. Understanding their mechanisms‚ indications (like periodontal infections or post-extraction complications)‚ and potential adverse reactions is paramount. Resources emphasize responsible antibiotic stewardship to combat resistance.
PDFs highlight the importance of accurate terminology when documenting prescriptions and discussing antibiotic therapy with patients. Proper usage‚ dosage‚ and duration are critical‚ alongside allergy considerations. Comprehensive guides aid in selecting the appropriate antibiotic based on infection type and severity.
Common Dental Procedures
Dental terminology PDFs cover restorative dentistry‚ endodontics‚ and periodontics‚ detailing procedures and associated terms for effective communication and documentation within practice.
Restorative Dentistry
Restorative dentistry‚ as outlined in dental terminology PDFs‚ focuses on returning teeth to their optimal function and form. This encompasses a wide range of procedures‚ including dental fillings to repair cavities‚ crowns to cover damaged teeth‚ and bridges to replace missing teeth.
Understanding the specific terminology – such as ‘composite‚’ ‘amalgam‚’ ‘porcelain-fused-to-metal‚’ and ‘fixed partial denture’ – is vital for accurate charting‚ treatment planning‚ and communication between dental professionals. PDFs often detail the nuances of each restorative technique‚ emphasizing precise language for clarity and legal documentation.
Endodontics
Endodontics‚ detailed within dental terminology PDFs‚ centers on the dental pulp and surrounding tissues. Primarily‚ it involves root canal therapy – a procedure to treat infected or inflamed pulp within a tooth. Key terms include ‘pulpitis‚’ ‘periodontal abscess‚’ ‘apicoectomy‚’ and ‘obturation.’
PDF resources emphasize precise terminology for describing the intricate anatomy of root canals and the steps involved in treatment. Accurate documentation‚ utilizing standardized terms‚ is crucial for successful endodontic procedures and clear communication amongst specialists.
Periodontics
Periodontics‚ as outlined in dental terminology PDFs‚ focuses on the prevention‚ diagnosis‚ and treatment of diseases affecting the supporting structures of teeth – gums and bone. Essential terms include ‘gingivitis‚’ ‘periodontitis‚’ ‘scaling and root planing‚’ and ‘periodontal pocket.’
These resources highlight the importance of precise language when charting periodontal conditions and describing treatment plans. Understanding terminology related to bone loss‚ attachment levels‚ and inflammation is vital for effective periodontal care and patient education.
Dental Specialties
Dental specialties‚ detailed in dental terminology PDFs‚ encompass focused areas like orthodontics‚ oral surgery‚ and pediatric dentistry‚ requiring specialized lexicon.
Orthodontics
Orthodontics‚ a specialized branch of dentistry‚ focuses on the alignment of teeth and jaws‚ as detailed within comprehensive dental terminology PDFs. Understanding specific terms like ‘malocclusion‚’ ‘braces‚’ ‘retainers‚’ and ‘cephalometrics’ is vital. These resources clarify procedures correcting bite issues‚ improving aesthetics‚ and enhancing oral function.
PDFs often illustrate orthodontic appliances and treatment phases‚ defining terms related to tooth movement and jaw growth. Mastery of this lexicon is essential for dental professionals and students alike‚ enabling precise communication regarding diagnosis and treatment plans within this specialized field.
Oral Surgery
Oral Surgery‚ a demanding dental specialty‚ requires a robust understanding of precise dental terminology‚ often detailed in specialized PDFs. Key terms include ‘extraction‚’ ‘impaction‚’ ‘alveoplasty‚’ ‘biopsy‚’ and ‘reconstructive surgery.’ These PDFs clarify procedures involving the mouth‚ jaws‚ and facial structures‚ addressing complex cases beyond general dentistry.
Resources define surgical techniques‚ post-operative care‚ and potential complications. Mastery of this terminology is crucial for accurate charting‚ treatment planning‚ and effective communication between surgeons‚ assistants‚ and patients‚ ensuring optimal surgical outcomes and patient safety.
Pediatric Dentistry
Pediatric Dentistry necessitates specialized dental terminology‚ often comprehensively outlined in dedicated PDF resources. Key terms include ‘eruption‚’ ‘shedding‚’ ‘habit breaking‚’ ‘fluorosis‚’ and ‘space maintainers.’ These PDFs detail the unique dental needs of infants‚ children‚ and adolescents‚ focusing on growth and development.
Understanding terminology related to behavior management‚ preventative care‚ and early intervention is vital. Accurate documentation‚ clear communication with parents‚ and appropriate treatment planning rely on a firm grasp of these specialized terms‚ ensuring positive dental experiences for young patients.